An asset protection trust is legal document allows a third party trustee to hold items of value and keep them away from judgment creditors. The document on which the trust is written is the trust deed. The trustee must act under the terms of the trust deed. In general, the trustee is duty-bound to carry out the intent of the settlor. The trustee acts in a fiduciary capacity for the trust beneficiaries. Thus, the purpose of an asset protection trust is to keep assets out of the hands of creditors. We compare both offshore and domestic options. These types of trusts are available in several US states, such as Nevada, Delaware and Alaska. Foreign countries, such as the Cook Islands, Nevis, Belize, as well as Hungary, offer some of the most protective statutes.
To get straight to the point, when you look at Offshore vs. Domestic trusts to shield yourself from lawsuits, offshore wins hands down. That is because your friendly neighborhood judge has the right to issue court orders to domestic trustees. The law does not grant that privilege to members of the local judiciary for offshore trusts. That is, the laws do not obligate the trustee in the foreign jurisdiction to comply.

Assets inside the trust are beyond the reach of the creditors of the trust beneficiary. The beneficiary is typically the one who has the right to receive the money from the trust. A creditor is, in this instance, someone who won a lawsuit against you. The settlor is the one who establishes the trust. Here you will find more information regarding what is an asset protection trust, and how it works.
Establishing an Asset Protection Trust
When you establish the trust, you decide whether or not you will also be a beneficiary of the trust. We also draft non-self-settled trusts such as children’s trusts. As the name implies, we set up this type of trust for the benefit of your children. Case law has demonstrated that neither your creditors nor those of your children can touch trust assets. You may be able to access trust funds through obtaining a loan from the trust. Then, we also establish self-settled trusts where you establish the trust and maintain beneficial interest in the trust.
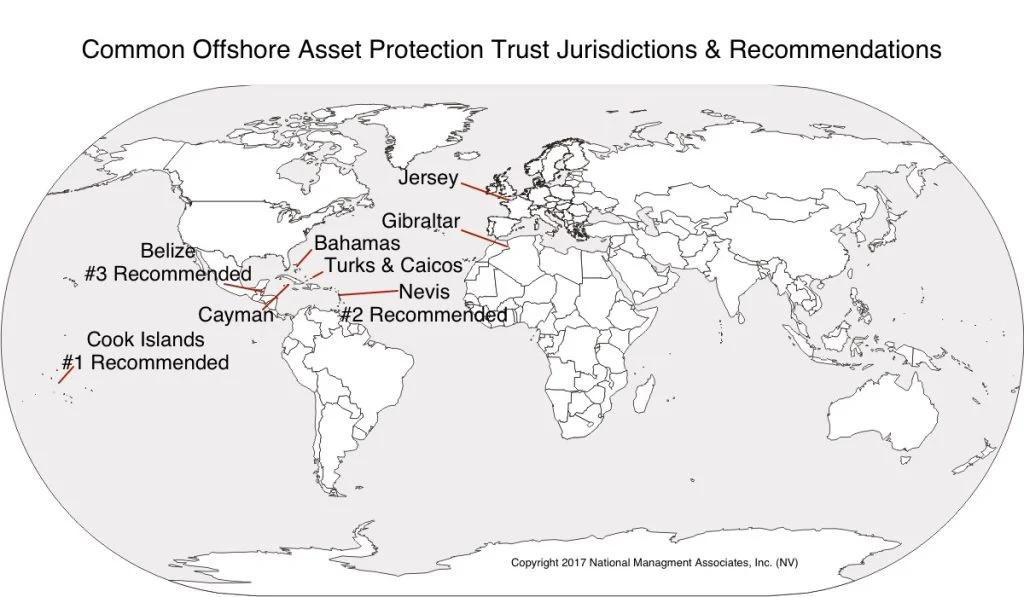
Certain jurisdictions are more favorable than others. Examples are offshore trusts include countries such as the Cook Islands, Nevis and Belize. Favorable US states include Nevada, South Dakota, Delaware and Alaska. There, you can form the trust, maintain beneficial interest, and statutorily enjoy protection from seizure.
Over the past 20 years, we have seen billions of dollars placed inside of offshore trusts. There are some choice foreign jurisdictions that have very favorable self-settled trust laws designed to protect assets. The chief of of these is the Cook Islands.
Domestic Asset Protection Trusts

In 1997 Alaska attempted to stop some of the outflow of funds and enacted self-settled trust statutes. Afterwards, Nevada, Delaware and South Dakota followed suit. Nevada and South Dakota are the two standouts with the most favorable statutes. This is mainly because one can shield the assets in as little as 6 months (in Nevada). So, the trusts protects assets six months from the date of reasonable discovery of transfer of assets into the trust. For example, publish the transfer of assets into the trust in a small local newspaper. Then, the trust protects the assets a half a year later.
Before these statutes went into place the only self-settled spendthrift trusts. A spendthrift trust is one in which the trustee can prevent creditors from taking trust funds. This can also keep a young beneficiary from wasting the money in the trust or spending it too quickly.
The US states who enacted these statutes also did away with the rule against perpetuities. This is an old British rule that limits the trust duration to the life of the person plus 21 years. Trusts formed in Nevada, Alaska, Delaware and South Dakota can continue forever.
Nevada Trust
Focusing on Nevada, here are some benefits of the Nevada Spendthrift Trust NRS 166.020.
A. The State of Nevada does not impose personal or corporate income tax.
B. If formed properly, a Nevada Irrevocable Spendthrift Trust is currently not subject to income taxes of other States.
C. A Nevada Spendthrift Trust is only subject to Federal Income Tax.
D. The Settlor can change beneficiaries, or subsequently add other beneficiaries at anytime. The Settlor does not need to notify any beneficiary past or present, the state of Nevada, or the Federal Government.
E. In Nevada, the statutes clearly define the rights and privileges of a Spendthrift Trust. As such, they do not depend on court decisions or interpretations for the validity of the Trust.
F. State of Nevada does not charge registration fees, annual reporting fees or fees for the Trust to remain valid. In addition, the statutes do not require such Trusts to maintain a Resident Agent in the State of Nevada.
Huge Disadvantage of Nevada Asset Protection Trusts
That said there is one huge disadvantage of Nevada asset protection trusts. This is a disadvantage for all domestic asset protection trusts, for that matter. They don’t work well unless you live in Nevada. Rather than speaking to Nevada asset protection trust promoters, study the case law. The case law clearly shows, over and over again, that local judges simply apply local laws.
“You are here. Your assets are here. I am going to apply the law here.” Signed, Your Friendly Neighborhood Judge. This is the pattern we see repeatedly with domestic asset protection trusts. The solutotion? Offshore asset protection trusts where the assets and the trustee are both beyond the reach of the local courts.
Asset Protection Trust Traits
The one who formed the trust is the settlor (a.k.a grantor). With the proper statutes, when the settlor is also a beneficiary, it can still provide asset protection. That is the case if the following is also true about the trust:
- It is irrevocable. This is because if the settlor could revoke (change) it, that gives the judge more control. The judge could order the settlor to change the beneficiary to his or her legal opponent.
- It has an independent trustee (not a blood relative, controlled employee or agent of yours).
- It does not require distributions of income or principal. (Instead, the payouts are subject to the trustee’s judgment.)
- It has a spendthrift clause.
The above are generally accepted requirements for self-settled spendthrift trusts. Moreover, the statutes of the modern US trusts of this type also state the following:
- That the the trust needs a trustee who lives in the state that regulates that trust. One can also use a bank or trust company that holds a license in that state.
- That some or all of the trust assets are in that state (such as a bank account).
- The trust documentation and the administration must be in the state.
Offshore Asset Protection Trusts
This is where the offshore trust shines above the domestic trusts. Bankruptcy is a federal action. The federal government has jurisdiction across all states. A domestic trust can survive bankruptcy with assets intact if the assets had been held in the trust for sufficient time, currently 10 years. That is because federal bankruptcy law obligates the courts to recognize exemptions provided for under various state laws. The problem is that few trusts can clear that hurdle.
However, experienced attorneys will tell you over and over again, not all judges rule according to law. Many rulings are by the judge’s gut feeling about the case. Once a judge renders a judgment, the judgment creditor can start seizing assets of the debtor immediately. They can do so even before an appeals court issues its ruling. Once your opponent seizes your assets, you have no resources left to pay an attorney. Thus, it may be difficult to find legal counsel to protect and defend you for free during the appeals process.
You may want to read our article entitled Asset Protection Trust Pros and Cons. We discuss the advantages and disadvantages of domestic and offshore asset protection trusts.
Bankruptcy Provisions
So, when there is a bankruptcy, which state’s laws apply? Suppose the court rules that Nevada or Delaware law applies because that is where the assets are located. Will the trust will shield the assets from bankruptcy? It depends. With modern statutes there is as ten year vesting period for assets. Within the ten-year time period, the courts consider trust assets part of the bankruptcy estate. That’s why we employ equity stripping strategies on domestic assets. We have seen this work effectively, and prevent the need for bankruptcy altogether.
Here is the problem. For those with a medium to large asset base, bankruptcy is usually a big mistake. It is a knee-jerk panic reaction to alleviate immediate pain. The problem is that it usually causes long-term agony. Don’t expect a bankruptcy attorney to reveal this truth. Bankruptcy strips you of your assets and destroys your credit.
The good news is that if you properly employ the appropriate asset protection trust, you can avoid bankruptcy altogether. We have seen many clients avoid a harmful Chapter 7 or Chapter 11 filing. They end up finding that bankruptcy is not necessary. This is because once they secure their holdings safely inside the proper asset protection trust, there is nothing for the creditor to take.
Offshore Vs. Domestic Trust in Bankruptcy
As of this moment in legal time, the results for the domestic trust don’t look good. Naturally, the judgment creditor will present arguments that try to penetrate a domestic trust. If it is a results-oriented judge, the judgment creditor will do just that. Naturally, when there are significant resources at stake, what will the creditor do? Fight even harder to challenge the legitimacy of a domestic trust.
However, what if the asset protection trust is in a foreign jurisdiction? Such as the Cook Islands or Nevis? Then, what if the assets inside the trust are located in a foreign bank account? The answer is that the properly drafted offshore trust deed has proven itself worthy to shield funds from creditors time and time again. On the other hand, suppose some of the assets are located in the US. We strip the equity from domestic assets, such as real estate, businesses and personal property.
For domestic real estate a land trust can work quite well to provide for privacy of ownership. A land trust is more of a privacy tool than one meant to shield assets. So, we also place equity stripping liens against the property. We have a third-party buyer who can buy those liens. They then place the proceeds into a you-can’t-touch-it account in the offshore asset protection trust trust.
In conclusion, filing bankruptcy is usually a big mistake. The offshore trust work extremely well when compared to bankruptcy. Why? Because with the proper asset protection trust one can retain one’s assets. As such, they can avert the need for bankruptcy altogether.
Case Law Example
We recently became aware of an unpublished Court of Appeals case in California: Kilker v. Stillman, 2012 WL 5902348 (Cal.App. 4 Dist., Unpublished, Nov. 26, 2012).[1]
Having endured attacks on the integrity of foreign asset protection trusts, in particular those from the Cook Islands, this case illustrates the vagaries of the us legal system and should be a clear warning to those same “doubters” of the potential pitfalls of a domestic asset protection planning in the U.S – particularly when measured against the well established laws of the Cook Islands. This case illustrates some important aspects that planners and their clients need to be wary of when putting in place a domestic asset protection plan, whereas the same concerns do not apply with regards setting up in an offshore foreign jurisdiction such as the Cook Islands.
While the court could have invalidated the structure the debtor used under several equitable legal theories, the court in the Kilker case made a determination as to whether there was a fraudulent conveyance AKA fraudulent transfer of property under the California Uniform Fraudulent Transfers Act (“UFTA”). It was a case of a leaking swimming pool built by its Homeowners on advice given by a Soils Engineer. The Homeowners successfully sued the Engineer, and moved to enforce judgment.
Why Domestic Trusts Don’t Work

After the pool was installed but years before any problem with the pool was detected, the Engineer had transferred assets to a Nevada domestic asset protection trust which he established without the help or advice from a lawyer. The Homeowners alleged that the Engineer’s transfer of an office building to the Trust was a fraudulent transfer under the UFTA. The Homeowners also claimed that the Trust was the alter ego of the Engineer. The engineer occupied the office building without a lease and rent free. In other words, none of the regular commercial formalities were employed. Moreover, when asked in his deposition to give the reason why he transferred his assets to an asset protection trust, the Engineer testified he did so for asset protection.
The Trial Court found that the Engineer was the alter ego of the Trust, and that the office building had been fraudulently transferred to the Trust as per the UFTA. The real kicker to the case though is that the Trial Court found that even though there was no existing “claim” at the time the Engineer made his transfers, the transfer was a fraudulent transfer because the Engineer made the transfers for the stated purpose of defeating the collection rights of unknown future claimants who might come along later.
Why Offshore and Not Domestic
From an asset protection point of view, this judgment has far reaching ramifications. Indeed, if you’re in the business of advising on wealth preservation or estate planning for those in high risk occupations and opt for the use of domestic asset protection trusts, (in preference to a foreign trust), then you need to be, well…worried.
Understandably, the Engineer and Trust appealed the Trial Court decision and argued that the fraudulent transfer laws are not meant to encompass claims against future, unknown creditors. But the Court of Appeals rejected the notion that the UFTA is limited to only existing creditors:
The statute does not include the terms ‘future creditor’ or ‘future potential creditors’ . . . and does not require that, from the debtor’s perspective, a creditor who challenges a transfer as fraudulent under the UFTA to have been reasonably foreseeable as the debtor’s creditor before pursuing remedies under the UFTA. Furthermore, the statute does not require that the debtor intended to hinder, delay, or defraud the specific creditor who challenges a transfer of an asset as violative of the UFTA. On the contrary, section 3439.04, subdivision (a) provides that a current creditor can challenge a transfer as fraudulent, regardless whether that creditor had a claim at the time of the transfer, if that creditor can prove, inter alia, the transfer was made to hinder, delay, or defraud any creditor.
For those who are not comfortable going offshore initially, there is a good option. It is called the Trigger Trust ®. The trigger trust is a domestic/offshore trust hybrid. You are an initial trustee, if you desire. If the legal need arises, your co-trustee can immediately pull the trigger to enact the offshore trust measures built into the trust.
Why Offshore Trusts Work
By comparison in the Cook Islands, there is no grey area when it comes to the issue of “future creditors” versus “present creditors”. Section 13B of our International Trust Act 1984 is very clear as to the rules to determine this important issue.
We leave it to our US colleagues to interpret the effects of the Kilker v Stillman decision. But lest to say that the Cook Islands is still considered the leading asset protection jurisdiction in the world, and can boast a long line of judicial precedent which upholds the integrity of the Cook Islands International Trusts Act 1984.
The bottom line is that US judges have jurisdiction over US trusts and trustees. They do not have jurisdiction over foreign trusts, trustees, and trust bank accounts held in financial institutions that do not have corresponding US branches. Time and time again experience has shown that parking funds in a properly structured offshore asset protection trust in the right jurisdiction simply works better than its domestic counterpart.
Asset Protection Trust Definition

The definition of an asset protection trust is as follows: An irrevocable trust drafted under the laws of specified jurisdictions that allows the same person be the settlor and discretionary beneficiary of the trust, yet protects the assets from the creditors of the settlor. Asset protection trusts are the most widely used legal vehicles for asset protection planning. When established in the proper jurisdiction, one may use asset protection trusts to effectively protect assets from creditors. They can also be useful to minimize the effects of taxation, divorce, or bankruptcy.
Asset protection trusts are particularly beneficial for those in high-liability professions, such as doctors and developers. Unfortunately, there is no shortage of money hungry plaintiffs looking for an easy pay day. Any wealthy individual who is interested in protecting what he or she has worked so hard to earn should consider establishing an asset protection trust.
What is an Asset Protection Trust?

People of means often utilize trusts to protect their assets. Asset protection trusts are trusts which divide the beneficial and legal ownership of assets. A trust’s beneficiaries are beneficial owners of equitable interests in the trust. However, the trustee holds the legal title of the assets, rather than the beneficiaries. The trust deed (document) directs the trustees actions. As a result, trusts enable their settlors to insulate assets from the claims of their creditors legally.
A key provision of asset protection trusts is a spendthrift clause. Professionals incorporate spendthrift language into the trust deed. The original concept is that the trust is created for the benefit of a person who is not able to control his or her spending. As a result, the settlor appoints an independent trustee to direct how the trust uses assets held therein. Today, settlors most commonly use this clause to protect assets from lawsuits. This is because the assets are under the control of the trustee rather than the settlor of the trust. Because the trustee, rather than the settlor is in charge, it generally protects these assets from the settlor’s creditors. When the judge orders the settlor to turn over the assets, the settlor can honestly say, “Sorry judge, I can’t.” Thus, the assets remain safe and secure within the trust.
A number of jurisdictions offer asset protection trusts. Asset protection trusts settled in the United States are often referred to as domestic asset protection trusts. Domestic asset protection trusts are offered only in certain states, such as Nevada, Delaware, and Alaska. When you compare domestic and offshore asset protection trusts, case law repeatedly shows that offshore trusts are more effective. That is, whereas domestic options can provide barriers to creditors, they are still within the reach of local courts.
Offshore asset protection trusts, such as those located in the Cook Islands, Nevis, or Belize, provide significant advantages over domestic asset protection trusts. Simply put, they work. Local judges do not have jurisdiction over offshore trustees. So, the these legal tools effectively tie the hands of your legal opponent.
Benefits of Offshore Asset Protection Trusts

Several jurisdictions, including the Cook Islands and Nevis, offer significant benefits for those seeking asset protection and financial privacy.
Ability to Wholly Own an LLC
One of the best ways to utilize a trust for asset protection is by forming the trust in conjunction with a limited liability company (LLC). Certain jurisdictions, such as the Cook Islands and Nevis, offer the option for an LLC to be wholly owned by a trust. The settlor of the trust transfers their assets to the LLC. The settlor serves as the manager for the LLC and, under normal circumstances, is able to control the assets. In the event of legal duress, the control of the LLC may be transferred to the trustee. Trustees in favorable jurisdictions are unable to respond to foreign judgments. As a result, assets are protected legally from the claims of creditors.
Estate Planning
The most popular jurisdictions for asset protection trusts, including the Cook Islands and Nevis, have no rule against perpetuities. This rule, active in most jurisdictions, limits the possible lifespan of the trust to just a few generations. As a result, the trusts in regions that have removed this restriction can be valuable assets for those looking to plan their estates across several generations. Furthermore, many of the favored jurisdictions do not recognize foreign judgments. This means that asset protection trusts are not subject to foreign inheritance laws.
Foreign Judgments Are Not Recognized
A significant benefit to settling a trust offshore is that most offshore haven jurisdictions do not recognize foreign judgments. If a domestic trustee is faced with contempt of court to release assets following a civil judgment, they will do so or face dire consequences. An offshore trustee, however, is not bound by US court orders. To pursue a judgment against the settlor of an offshore trust, a creditor must usually have the case re-adjudicated. This is because the trustee is only bound by the law of the jurisdiction where the trust was established. Some jurisdictions, such as the Cook Islands, Belize, and Nevis, provide additional barriers to keep creditors from attacking their trusts. These barriers may include requirements that the plaintiff travel to the jurisdiction to file suit. The courts may also charge large fees to open cases in these jurisdictions.
Even if a case is filed, it is unlikely that a creditor will be able to touch the assets held within an offshore trust. In many jurisdictions, the only time a creditor can touch the assets is in a proven case of fraudulent conveyance. The burden of proof is on the creditor to show that assets were transferred with the willful intention of shorting that specific creditor. The creditor must also prove that transferring those assets made the settlor insolvent.
Access to Assets Under Legal Duress
If properly established, asset protection trusts allow settlors to access assets while under legal duress. While a settlor is under legal duress, the trustee retains control of the assets held within the LLC in the trust. The trustee is not allowed to comply with foreign court orders. They may, however, pay bills for the settlor or pay a trusted friend or relative for the settlor.
Financial Privacy
Trustees of domestic trusts are routinely deposed or compelled by subpoena. They are subject to the judgments of US courts. US laws often require the disclosure of sensitive financial documents during legal proceedings. In contrast, many offshore jurisdictions consider the settling of trusts to be a private matter. The Cook Islands, for example, does not even require trusts to register the names of their settlors. Only the name of the trust, the name of the trustees, and the date of the trust deed are required to be registered.
Uses for Asset Protection Trusts

Asset protection trusts can be used to hold a wide variety of assets. They are frequently used to hold intellectual property, life insurance policies, and other types of assets. Both liquid and tangible assets may be held in asset protection trusts. It is also possible to hold real estate in an asset protection trust. However, it is important for US citizens to note that American real estate held in an offshore trust may still be affected by judgments levied in America. So, we record equity line of credit mortgages against those properties. An offshore lender buys them as needed and deposits the proceeds into an inaccessible account in the offshore trust. Liquid assets in the offshore trusts may prove tremendously beneficial for American settlors of in the event that the settlor experiences legal duress.
Assets may be transferred to the trust or the LLC held by the trust at the time the trust is settled. Assets may also be transferred to the trust or LLC at any time other. A settlor is best served when he or she transfers assets when they have or are immediately anticipating claims on those assets. This is best to avoid claims of fraudulent conveyance of assets. However, fraudulent conveyance, (now commonly called a voidable transaction) is merely a civil matter, not criminal. Thus, many, if not most, most clients successfully transfer assets after the fact.
You do not need to hold assets in the Cook Islands or Nevis. You can keep them in any financial institution in the world which provides a financial safe haven. Trustee involvement may be required depending on the type of assets you transfer into the trust. Trustee(s) may be required to sign transfer documents. Their signatures may also be required to open accounts.
As described above, asset protection trusts are often formed in conjunction with limited liability companies (LLCs). It is also possible to open trusts in tandem with a limited partnership (LP). In this situation, the assets are transferred to the partnership. The settlor of the trust receives 1% partnership interest for transferring their assets to the trust and acts as general partner. In turn, the settlor will transfer 99% partnership interest to the trust as a limited partner. Professionals suggested the LP approach in the past prior to widespread LLC legislation.
Structure of an Asset Protection Trust
Offshore trusts are generally comprised of four different roles. The names of these roles may vary based on the jurisdiction where the trust is established.
Settlor
The settlor of a trust is the person who first establishes the trust.
Trustee(s)
The trustee(s) hold the title to the assets which are held by the trust. Additionally, trustees are responsible for administering the trust. In certain jurisdictions, it is possible for trusts to own LLCs in their entirety. These LLCs may hold assets including bank accounts. In these jurisdictions, the most popular of which are the Cook Islands and Nevis, control of the LLC owned by the trust may be transferred to the trustee(s). When using this strategy for asset protection, it is beneficial to have only one trustee. However, many jurisdictions allow for multiple trustees.
Custodian
Trust custodians are optional positions in most jurisdictions. Custodians provide additional security to trusts by providing checks and balances to the power of the trustee. Custodians have the ability to appoint trustees. They may also veto decisions made by trustees on the settlor’s behalf. The custodian is generally a person whom the settlor trusts, such as a family member.
Beneficiary
A beneficiary of a trust is any person who receives benefit from the trust. Most often, beneficiaries of a trust include the settlor of the trust and/or their family members.
Conclusion

Most experts in the field call the asset protection trust the strongest means of securing wealth from creditors. Offshore asset protection trust beat their domestic competitors. This is because local judges do not hold jurisdiction over trustees who reside abroad. If you want to form an asset protection trust, fill out the inquiry form on this page or utilize the phone numbers on this page.